문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/14888
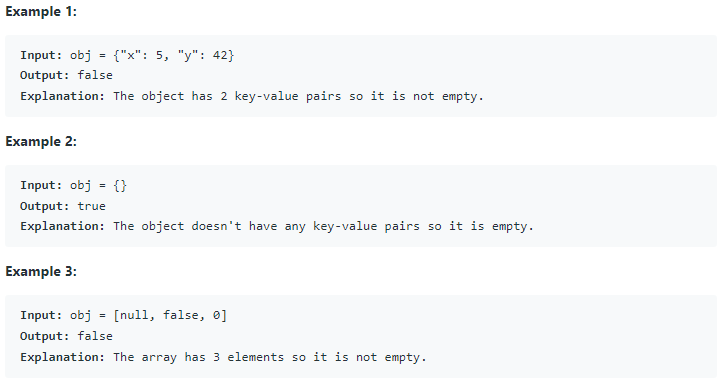
N개의 수로 이루어진 수열 A1, A2, ..., AN이 주어진다. 또, 수와 수 사이에 끼워넣을 수 있는 N-1개의 연산자가 주어진다. 연산자는 덧셈(+), 뺄셈(-), 곱셈(×), 나눗셈(÷)으로만 이루어져 있다.
우리는 수와 수 사이에 연산자를 하나씩 넣어서, 수식을 하나 만들 수 있다. 이때, 주어진 수의 순서를 바꾸면 안 된다.
예를 들어, 6개의 수로 이루어진 수열이 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6이고, 주어진 연산자가 덧셈(+) 2개, 뺄셈(-) 1개, 곱셈(×) 1개, 나눗셈(÷) 1개인 경우에는 총 60가지의 식을 만들 수 있다. 예를 들어, 아래와 같은 식을 만들 수 있다.
- 1+2+3-4×5÷6
- 1÷2+3+4-5×6
- 1+2÷3×4-5+6
- 1÷2×3-4+5+6
식의 계산은 연산자 우선 순위를 무시하고 앞에서부터 진행해야 한다. 또, 나눗셈은 정수 나눗셈으로 몫만 취한다. 음수를 양수로 나눌 때는 C++14의 기준을 따른다. 즉, 양수로 바꾼 뒤 몫을 취하고, 그 몫을 음수로 바꾼 것과 같다. 이에 따라서, 위의 식 4개의 결과를 계산해보면 아래와 같다.
- 1+2+3-4×5÷6 = 1
- 1÷2+3+4-5×6 = 12
- 1+2÷3×4-5+6 = 5
- 1÷2×3-4+5+6 = 7
N개의 수와 N-1개의 연산자가 주어졌을 때, 만들 수 있는 식의 결과가 최대인 것과 최소인 것을 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫째 줄에 수의 개수 N(2 ≤ N ≤ 11)가 주어진다. 둘째 줄에는 A1, A2, ..., AN이 주어진다. (1 ≤ Ai ≤ 100) 셋째 줄에는 합이 N-1인 4개의 정수가 주어지는데, 차례대로 덧셈(+)의 개수, 뺄셈(-)의 개수, 곱셈(×)의 개수, 나눗셈(÷)의 개수이다.
출력
첫째 줄에 만들 수 있는 식의 결과의 최댓값을, 둘째 줄에는 최솟값을 출력한다. 연산자를 어떻게 끼워넣어도 항상 -10억보다 크거나 같고, 10억보다 작거나 같은 결과가 나오는 입력만 주어진다. 또한, 앞에서부터 계산했을 때, 중간에 계산되는 식의 결과도 항상 -10억보다 크거나 같고, 10억보다 작거나 같다.
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
// 0 -> + 기호
// 1 -> - 기호
// 2 -> x 기호
// 3 -> ÷ 기호
public class Main {
static int[] numbers;
static int[] picked;
static LinkedList<Integer> operators; // 연산자 모음
static boolean[] visited; // 연산자 방문 여부 저장
static int N;
static int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
numbers = new int[N];
visited = new boolean[N-1];
picked = new int[N-1];
operators = new LinkedList<>();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
numbers[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int cnt = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for(int j = 0; j < cnt; j++){
operators.push(i);
}
}
permutation(0);
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println(min);
}
/**
*
* @param cnt : 현재까지 선택한 요소의 개수
*/
static void permutation(int cnt){
if(cnt == N-1){
getMinMaxValue();
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < N-1; i++){
if(visited[i]) continue;
visited[i] = true;
picked[cnt] = operators.get(i);
permutation(cnt+1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
static void getMinMaxValue(){
int value = numbers[0];
for(int i = 0; i < N-1; i++){
value = calculate(value, numbers[i+1], picked[i]);
}
if(value < min) min = value;
if(value > max) max = value;
}
static int calculate(int num1, int num2, int operator){
int result = 0;
switch (operator){
case 0:
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case 1:
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case 2:
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case 3:
result = num1 / num2;
break;
}
return result;
}
}
순열로 문제를 풀었다. 각 연산자를 0, 1, 2, 3으로 맵핑하였고, caculate 함수에서 num1과 num2를 계산해주었다. 또한 getMinMaxValue() 함수에서 value 값을 누적해가며 최종 값을 계산하였고, min과 max 값을 갱신하였다.